Templates
Whether you’re a seasoned freelancer, a successful small business owner, or just earning some extra cash on the side, a professional invoice is an essential part of doing business. Start with a customizable template
By Type
What Is an Invoice?
An invoice is a formal request for payment. Like a bill from a utility company or a check from a restaurant, the purpose of an invoice is to describe in detail the services rendered or goods sold, the balance owed, and the terms of payment.
Depending on the terms of the engagement, the recipient of an invoice can arrange to pay the invoice with a check, wire transfer, or another method of payment. Digital invoices allow clients to pay directly through a variety of online platforms.
What To Include On an Invoice
Invoices don’t need to be complicated, but they do need to include several critical pieces of information in order to be considered legitimate. The following components ensure that all the relevant details of the transaction are presented in a clear and concise way. Layout and design are also important to consider. Use a template or generator to take the guesswork out of the process.
Invoice Header
The word “Invoice” should be labeled clearly at the top of the document.
Sender Information
The sender’s name and contact details, as well as the company name (if applicable), should be featured in the “Bill From” section.
Recipient Information
Include the invoice recipient’s information in the “Bill To” section, including the company name, contact details, and the name of a specific point of contact if possible.
Invoice Number
Each invoice should have a unique number for organizational purposes. This can be assigned at the seller’s discretion.
Itemized Description(s)
Include an itemized list of all goods/services rendered with a detailed description and cost-per-unit for each item.
Balance Due
The total balance owed should be featured prominently in any invoice. Be sure to show the subtotal and any applicable taxes, fees, and discounts.
Terms and Conditions
The payment instructions and due date should be made clear in the invoice, along with any other terms and conditions.
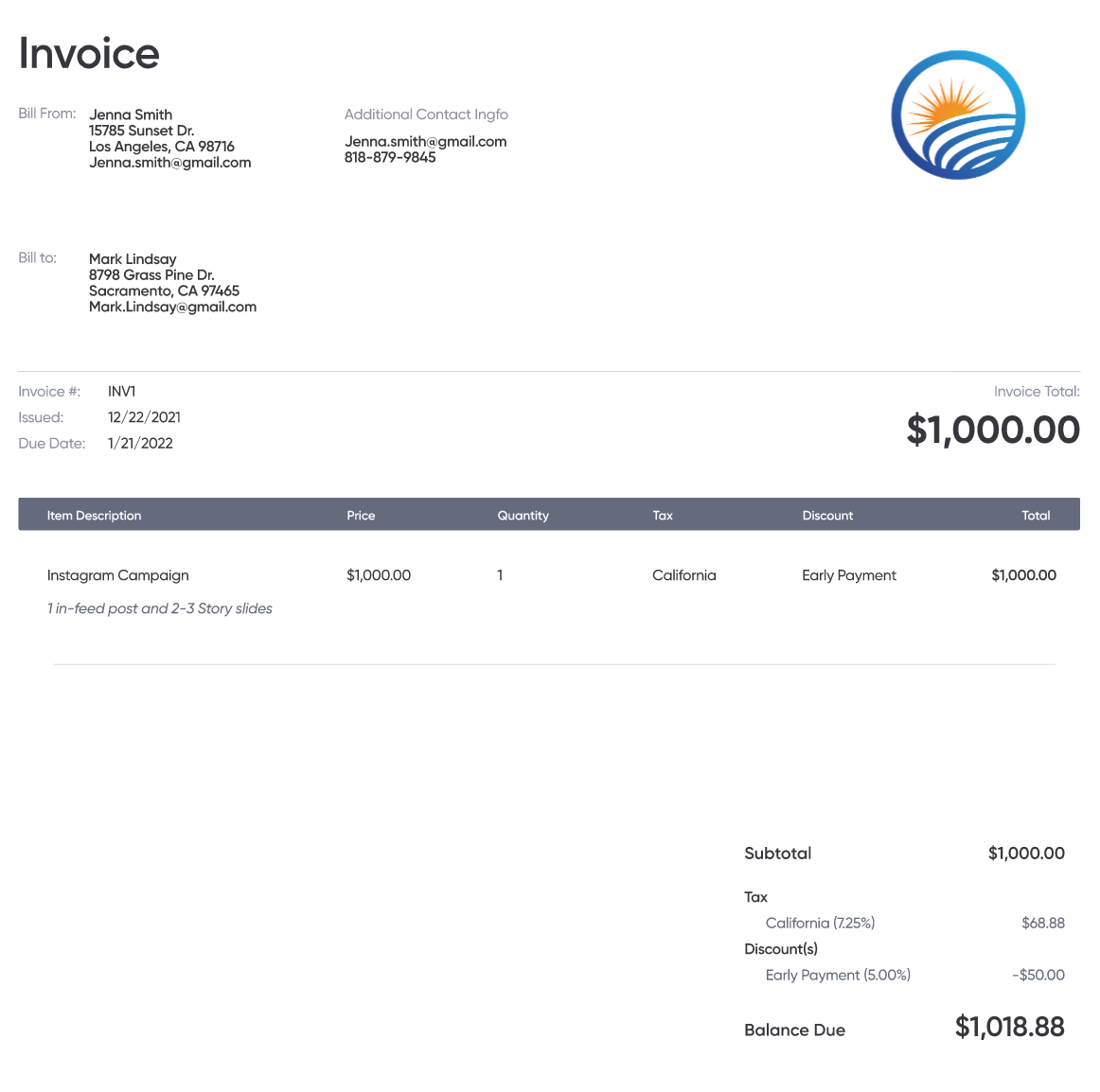
Invoice Generator vs. Invoice Templates
Invoice templates are pre-designed documents that can be downloaded and customized to the user’s needs. A third-party app, such as a PDF editor or word processor, is required to edit the fields manually.
An invoice generator is a software tool that streamlines this process by creating a custom invoice based on user input. The fields are automatically populated with data the user is prompted to enter, saving time and reducing errors in the process.
One important benefit of using an online invoice generator is direct integration with payment processing platforms. This allows the recipient to immediately pay the invoice according to options offered by the seller, such as credit card, ACH transfer, or digital wallets.